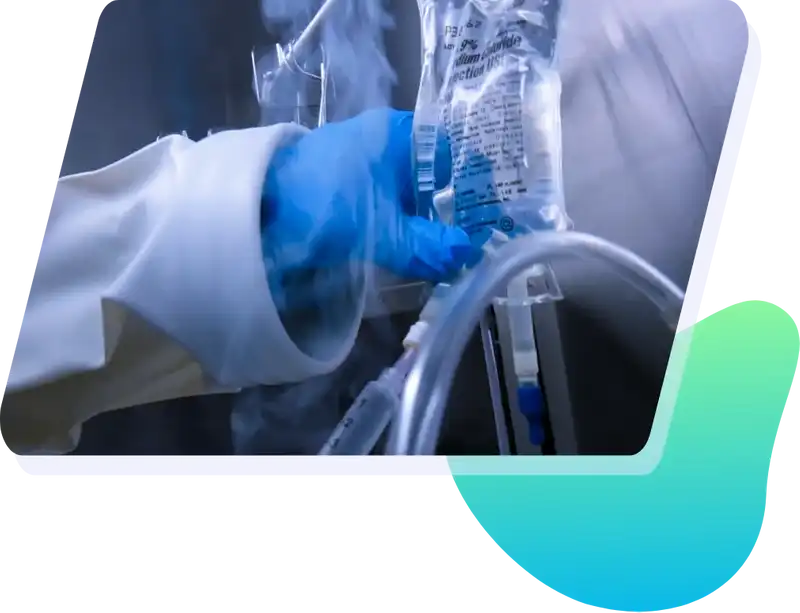
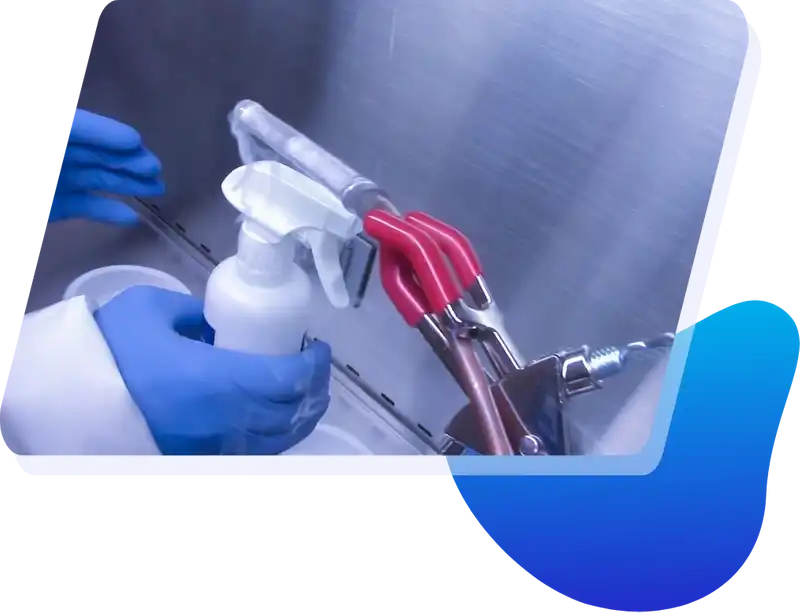
Compounding Aseptic Isolators Certification Tests
Let our team of experts keep your lab safe by becoming your Compounding Aseptic Isolator service provider. Services include testing, certification, emergency repair and Maintenance. Our certification tests include:
- Inflow Velocity Measurements
- Down-Flow Velocity Measurements
- HEPA Filter Integrity Testing
- Control Installation and Service
- Ante Chamber Inspection
- Smoke Pattern Testing
- Alarm Calibration
- Site Installation
Compounding Aseptic Isolators Reports
The isolators must be proven to maintain ISO Class 5 air quality during material transfer and under dynamic operating conditions. Following certifications, you will receive a full report of each test performed on your CAI in the field. All testing equipment is calibrated to N.I.S.T. standards within the previous 6 calendar months.
Our Certifications
Accutrol Controls
Aircuity Controls
Antect Controls
Phoenix Controls
NSF Accredited Biosafety Cabinet Certifiers
NEBB Quality Certified
ASHRAE 110 Certifications
BSL-3 Certification
How frequently do I need to certify my CAI?
USP 797 states that isolators need to be certified per CETA CAG-002-2006. This document requires certification upon installation, every six months, when moved, and when a major service is performed.
USP 797/800 Compliance Updates
The most recent update to these regulations effect:
- Calibrations, certifications and qualifications of equipment and classified areas
- Requirements for certification of classified clean room areas
- Testing performed as part of the facility certification
- Scenarios requiring investigations and corrective actions
- Vented biological safety cabinet requirement
- Containment secondary engineering control (C-SEC)
- Control requirements
The compounding of drugs, both sterile and non-sterile are constantly undergoing rapidly evolving state standards under the FDA and USP. Compliance under these regulations is critical for the safety of technicians and patients. BalCon helps you navigate those complexities without worry.
According to the draft revision of USP 797, compounding aseptic isolators will be divided into two classifications: Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS) and Isolators. The FDA and USP are continually working to strengthen the enforcement of these units.
How frequently should CAI sleeves be changed?
Compounding isolators often utilize a glove system to provide complete containment while manipulating sterile compounds. We recommend you follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and consider how often the unit is used. It is important to watch for small pin holes and adopt a process for tracking particle counts in negative pressure isolators.
Positive Pressure vs Negative Pressure
Positive pressure CAIs are used when no hazardous drugs are being manipulated. In this instance, the unit has a greater atmospheric pressure than the outside environment. This results in ISO Class 5 operating conditions.
Negative pressure CAIs are used when hazardous drugs compounds are present. The unit operating pressure is less than atmospheric pressure in these instances. This too results in ISO Class 5 operating conditions.