Annual Inspections and Maintenance
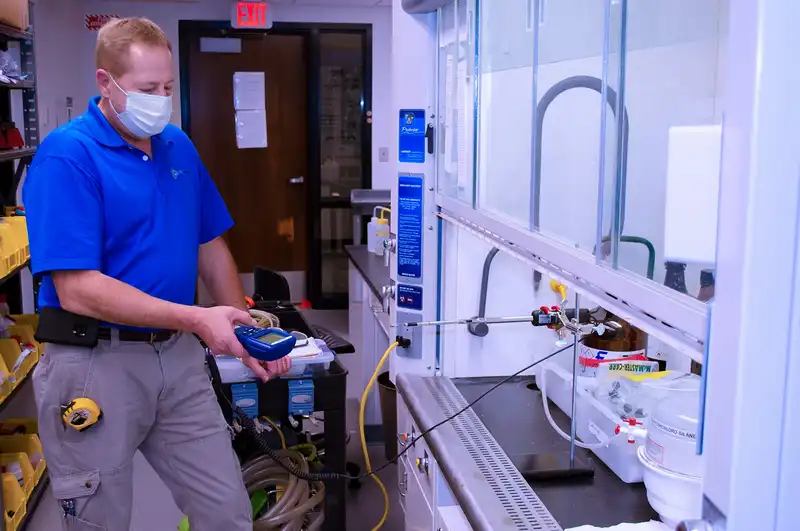
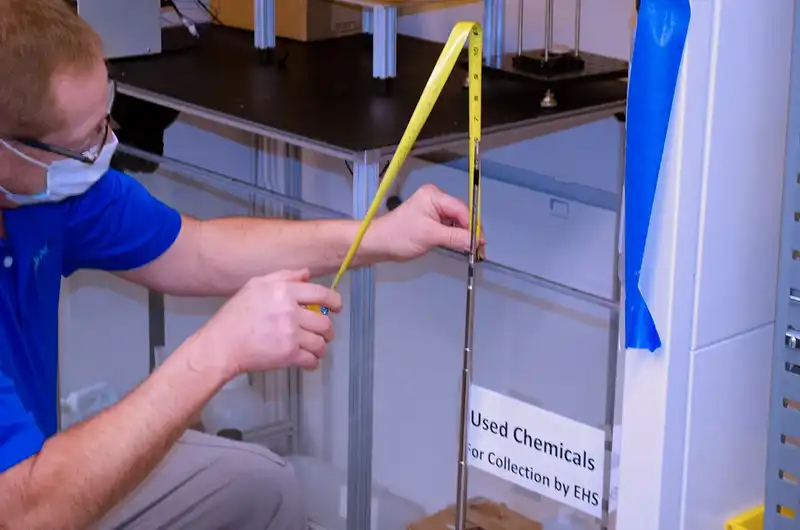
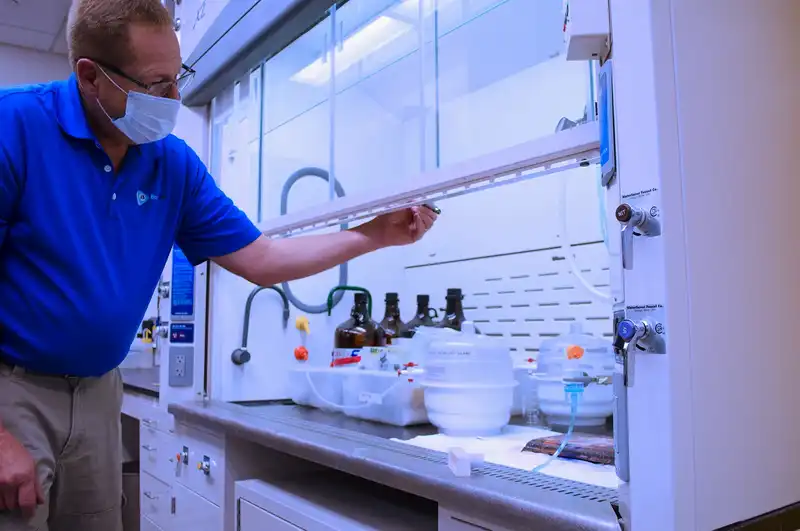
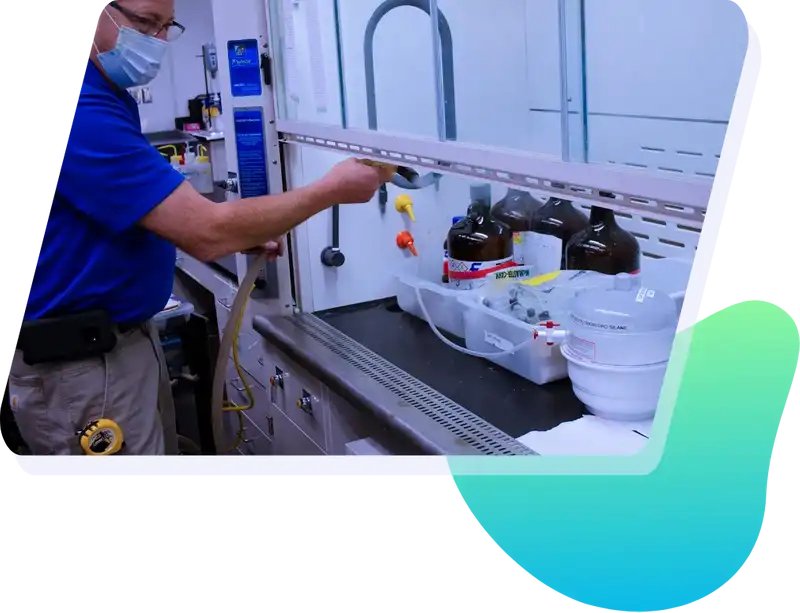
Our Lab Safety team performs annual inspections, routine maintenance, service, and repair on all fume hood classes. Using Airflow monitoring equipment our certified experts can ensure the safety and efficiency of your lab. Whether its problems with baffles, blowers, air loss, filtration, or controls, we have a fix. Fume Hood Certifications should be certified at least once per year to ensure they are running with correct airflow levels and airflow patterns. Annual inspections and routine maintenance commonly include:
- High/Low Flow Alarm Testing and Calibration
- Internal Pressure Monitoring
- Hood Face Velocity Testing
- Visualized Air Flow Testing (Smoke Testing)
- SASH Inspection
- Critical Controls Verification
- Fume Hood Installations
- Laboratory Relocations and Renovations
- 24/7 Emergency Response Services
ASHRAE 110 Fume Hood Tests
ASHRAE 110 is the preferred method for testing the performance of laboratory fume hoods. It is important to note, that this certification does not directly affect safety. Instead, this standard gives guidelines to meet when performing quantitative tests for fume hoods. These tests include:
- As Manufactured (AM): The fume hood is built, assembled, and tested by the manufacturer at their facility.
- As Installed (AI): The fume hood is installed at the location of the customer. This ventilation system is tested and balanced with no fumes in the fume hood's final location.
- As Used (AU): The fume hood is tested and balanced after it has been in use by the customer.
ASHRAE 110 Fume Hood Certifications
Inflow Face Velocity Profiling
This test ensures the hood can contain fumes without causing turbulence between the face of the hood and the operator.
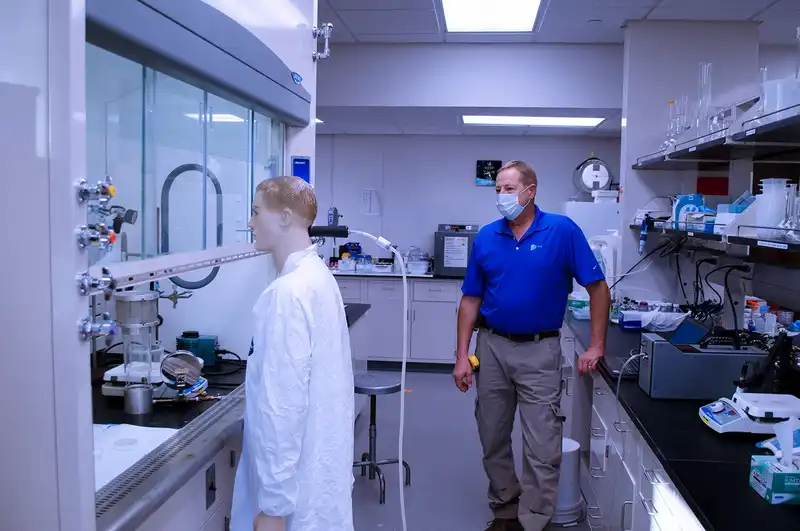
Tracer Gas Containments
Using a dispersion device, we release a tracer gas like sulfur hexafluoride inside the fume hood. The performance of the hood is determined by measuring the concentration of the tracer gas the breathing zone.
Cross-Draft Testing
A fume hood's effectiveness is dependent on the environment of the fume hood. If there are drafts in this space, they can create turbulent air pockets and the draw the contaminants from the hoods. Cross-draft testing mitigates this risk.
Airflow Smoke Pattern Testing
This is the final test in the certification process. The test certifies unidirectional airflow of the hood to the High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters.
Variable Air Volume (VAV) Response Testing
To conserve energy, some fume hoods come equipped with VAV (Variable Air Volume) systems. These types of hoods are designed to modulate air flow to a minimum when the sash is closed or when the hood is unoccupied. Special airflow tests are required to evaluate proper operation of the VAV's flow control systems.
Sash Motion Effect (SME) Test
The performance of the fume hood is measured by the maximum positional sash movements over a period of time.
Understanding Face Velocity vs Visual Testing
Face Velocity Testing is the average amount of air that is pulled through the chemical hood. If these velocities are too low then chemical fumes will escape the hood into the lab. If the velocities are too high, energy costs will be high as you exhaust large amounts of conditioned air from the room. A traditional hood should be between 80 and 100 FPM according to many agencies. This may increase to 120 if you're working with highly toxic chemicals.
While a face velocity tests can determine airflow rates, smoke testing is the final authority on whether your hood is functioning appropriately. This is because diffusers and room pressure as well as a number of other factors can affect the containment in a fume hood. That is also why a smoke test is the final step in the certification process.
Fume Hood Maintenance Checklist
For any lab manager, conducting check-ups on your labs critical safety equipment is essential to keeping your lab running the way it was designed. To ensure you don’t miss a step, we created this fume hood checklist to ensure your labs are running safely.